
Inspiring Education & Travel
Toll Free Numbers from
- USA: 1-866-514 7479
- UK: 01800 404 9800
- Australia: 0-1800-603-827
- Canada: 1-877-442 0843
- New Zealand: 01800441330
Contact us
9:00 AM - 7:00 PM
10:00 AM - 3:00 PM CST
- HOME
- ABOUT ITTO
-
TEFL COURSE DESTINATIONS

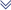 ITTO School's Map
ITTO School's Map MEXICO
MEXICO Guadalajara
Guadalajara Puerto Vallarta
Puerto Vallarta Chiapas
Chiapas Playa del Carmen
Playa del Carmen ARGENTINA
ARGENTINA Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ITALY
ITALY Florence
Florence CANADA
CANADA Toronto
Toronto Vancouver
Vancouver CHINA
CHINA Shanghai
Shanghai COSTA RICA
COSTA RICA Manuel Antonio
Manuel Antonio Playa Samara
Playa Samara CZECH REPUBLIC
CZECH REPUBLIC Prague
Prague FRANCE
FRANCE Toulouse
Toulouse GUATEMALA
GUATEMALA Antigua
Antigua PERU
PERU Cusco
Cusco SPAIN
SPAIN Barcelona
Barcelona Madrid
Madrid THAILAND
THAILAND Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai USA
USA New York
New York Chicago
Chicago Miami
Miami Online TEFL Programs
Online TEFL Programs Compare Course Features
Compare Course Features
- WHAT IS TEFL?
- REVIEWS
- CONTACT US
- SPECIAL FINANCING OPTION















